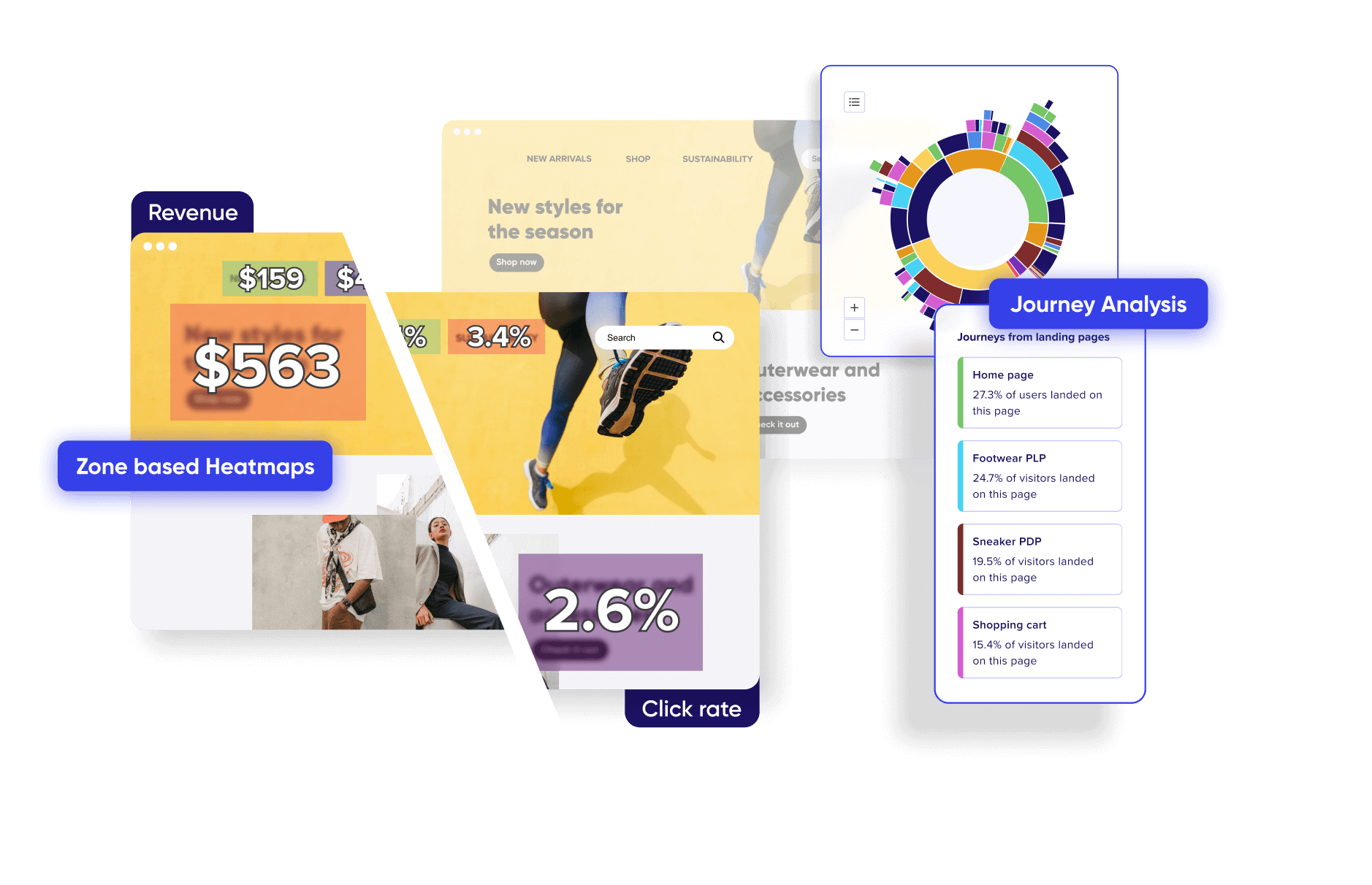
Know what drives engagement and abandonment on your sites and mobile apps.

Creating a customer journey map in the context of retail banking is a strategic initiative that enhances the customer experience. The process begins with the identification of the customer persona. This involves a detailed analysis of the customer’s demographics, banking preferences, and financial needs. It is crucial to understand the customer’s motivations, challenges, and goals to effectively cater to their needs.
The second step involves outlining the stages of the customer’s journey. This includes the awareness stage, where the customer first becomes aware of the bank’s financial services, the consideration stage, where the customer evaluates the bank’s offerings, the decision stage, where the customer chooses to bank with the institution, and the advocacy stage, where the customer becomes a loyal patron and recommends the bank to others.
The third and fourth steps involve identifying the key customer touchpoints and the customer’s goals at each stage. Touchpoints are the various points of interaction the customer has with the bank, such as visiting the bank’s website, speaking to a customer service representative, or using the bank’s digital banking services. The customer’s goals may include tasks they aim to accomplish, such as completing a transaction process, applying for a loan, or setting up a direct deposit. The fifth step involves mapping out the customer’s emotions at each stage of their journey.
This is crucial in understanding the customer’s experience and identifying areas for improvement. The sixth step involves identifying the moments of truth, which are significant interactions that can make or break the customer’s relationship with the bank.
The final step involves taking action based on the insights gained from the customer journey map. This may involve making changes to improve the customer experience, tracking the effectiveness of these changes, and consistently refining the customer journey map based on new insights and customer feedback.
In the realm of retail banking, defining customer segments is a critical process that enables banks to understand and cater to the diverse needs of their customers. This process involves dividing the customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics such as age, income level, banking habits, and financial goals.
By defining these segments, banks can tailor their products, services, and communication strategies to meet the specific needs of each group. For instance, a segment of young professionals may prioritize digital banking services and financial products that assist in managing student loans. Conversely, a segment of retirees may value in-person customer service and products that offer stable investment returns.
Know what drives engagement and abandonment on your sites and mobile apps.
By understanding these distinct segments, banks can develop targeted marketing strategies, design products and services that meet the unique needs of each segment, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, defining customer segments allows banks to gain a deeper understanding of their customer base. It provides insights into the preferences, behaviors, and needs of each segment, enabling banks to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and customer service initiatives. Furthermore, it allows banks to track the performance of each segment, identify trends and patterns, and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Customer journey mapping in retail banking is a strategic tool that allows banks to visualize and understand the customer’s experience from their perspective. The journey map traces the customer’s path from their first interaction with the bank, through their engagement with the bank’s financial services, and into a long-term banking relationship.
By mapping out this journey, banks can identify opportunities for improvement, enhance customer satisfaction, and increase customer retention rates. A customer journey map typically includes the stages of the customer’s journey, the customer’s goals at each stage, the touchpoints or interactions the customer has with the bank, the customer’s emotions at each stage, and the moments of truth.
By understanding these elements, banks can design and deliver a customer experience that meets and exceeds customer expectations. Furthermore, a customer journey map is not a static document.
It should be regularly updated and refined based on new insights, changes in customer behavior, and feedback from customers. This ensures that the map accurately reflects the current customer experience and continues to provide valuable insights for improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer journey mapping in retail banking is a strategic process that involves creating a visual representation of the customer’s experience from their perspective. It traces the customer’s journey from their initial interaction with the bank, through their engagement with various banking services, and into a long-term banking relationship. The customer journey map includes various elements such as the stages of the customer’s journey, their goals at each stage, the touchpoints or interactions they have with the bank, their emotions throughout the journey, and the critical moments of truth. By understanding and analyzing these elements, banks can gain valuable insights into the customer’s needs, preferences, and pain points.
Know what drives engagement and abandonment on your sites and mobile apps.
Furthermore, customer journey mapping allows banks to identify areas of improvement in their customer experience. By pinpointing the stages of the journey where customers experience difficulties or dissatisfaction, banks can take targeted action to improve these areas. This could involve enhancing the usability of their website, improving their customer service, or refining their product offerings.
Finally, customer journey mapping in retail banking is not a one-time process.
It requires ongoing monitoring and refinement to ensure that the map accurately reflects the evolving customer experience. This involves gathering regular feedback from customers, analyzing customer behavior data, and staying abreast of changes in the banking industry and customer expectations. This continuous refinement ensures that the customer journey map remains a valuable tool for improving the customer experience and driving business growth.
Customer journey mapping has become a cornerstone in the banking operations, providing a detailed perspective of the customer experience.
This process visually represents the customer’s interactions from the initial contact to long-term engagement, focusing on the key customer touchpoints. In the realm of financial services, understanding the customer’s journey is critical to meet and exceed customer expectations, address their needs, and mitigate potential frustrations.
The advent of digital banking has amplified the number of customer touchpoints, adding complexity to the customer journey. From online transactions to mobile banking apps, these touchpoints are integral parts of the transaction process.
Understanding this journey is crucial for banks to deliver an optimized customer experience. Customer journey mapping identifies gaps in services, enabling banks to enhance their customer service. For example, if a customer encounters difficulties during the transaction process on a mobile banking app, the journey map will highlight this issue, prompting the bank to make necessary improvements.
Know what drives engagement and abandonment on your sites and mobile apps.
Moreover, customer journey mapping is a strategic tool for anticipating the future needs of customers. By analyzing past interactions and behaviors, banks can predict future requirements, enabling them to proactively develop and offer services or products tailored to these needs. This forward-thinking approach not only improves the customer experience but also fosters customer retention.
It also presents opportunities for cross-selling and up-selling, which can significantly boost a bank’s position in the sales funnel. Lastly, customer journey mapping is a strategic instrument for differentiation in the competitive banking sector.
By delivering a superior customer experience informed by customer feedback and a deep understanding of the customer’s journey, banks can increase customer retention. This not only helps to maintain a competitive edge but also contributes to the growth of the bank’s position in the sales funnel.
In conclusion, customer journey mapping is not just a tool for improving customer service, but a strategic instrument that drives business performance.
Know what drives engagement and abandonment on your sites and mobile apps.